스포트라이트
Business Records Manager, Certified Document Imaging Architect, Document Control Manager, Document Management Consultant, ECM Consultant (Enterprise Content Management Consultant), Electronic Content Manager, Record Systems Analyst, Records and Information Management Consultant (RIM Consultant), Records and Information Management Specialist (RIM Specialist), Records Manager, File and Document Manager
No matter what its mission is, every organization has one thing in common—documents!
From creation to completion, documents have a lifecycle that must be managed so they don’t get lost, mishandled, or mixed up. But with so many people generating, routing, and handling documents, it’s easy to lose track quickly. That’s why organizations hire Document Management Specialists to take care of things!
These specialists set up efficient, organized workflows so physical and electronic documents are properly categorized, tracked, and safeguarded. They also help to format and edit documents, assemble various documents into packets, and route them to individuals or departments for review and comments. Sensitive documents may be dated and time-stamped as they make their rounds, to ensure a traceable audit trail is available.
Once all actions are finished, the documents are considered “records” and cannot be further altered. These records are then filed in accordance with the organization’s records management policies.
- Ensuring documents are managed effectively
- Supporting the operational backbone of the employing organization
- Opportunities to work in a huge range of industries
근무 일정
- Document Management Specialists generally work full-time, with some overtime occasionally required.
일반적인 의무
- Develop procedures for document life cycle management
- Create document classification taxonomies. Classify documents according to their characteristics
- Implement metadata management for easy document retrieval
- Customize document management system features and workflows
- Ensure document systems integrate with other organizational software
- Utilize data capture technology for document importation
- Convert physical documents to digital ones, ensuring accuracy and searchability
- Assess document management needs of departments or end users
- Train staff on effective document management, emphasizing security practices
- Ensure document management systems are secure but accessible to those who have a need and authorization to access them
- Monitor document access and permissions. Maintain confidentiality and privacy
- Implement version control measures if documents are routinely revised
- Route documents for review and comments
- Format and edit documents, if requested
- Assemble documents that need to be kept together, such as contracts with addendums or forms
- Require audit trails for sensitive documents being routed
추가 책임
- Monitor compliance with document management regulations
- Check documents in and out of storage
- Stay updated on management technologies and best practices
- Collaborate with records managers to retain, archive, and dispose of documents
- Create disaster recovery plans for the document systems
- Analyze system performance to recommend enhancements
- Coordinate document migrations during system upgrades
- Conduct audits to maintain integrity, addressing discrepancies
- Support users with electronic content access issues
- Create user manuals and training materials
소프트 스킬
- 세부 사항에주의
- 기밀 유지
- 조정
- 비판적 사고
- 고객 서비스
- 근면
- 독립
- 대인관계 및 커뮤니케이션 기술
- 모니터링
- 문제 해결
- 팀워크
기술 능력
- Proficiency in document management software (e.g., SharePoint, OpenText Documentum)
- Knowledge of scanning technologies
- Experience with Content Management Systems, metadata, and classification systems
- Familiarity with version control practices
- Skills in data entry, data capture, database management, and querying
- Understanding of workflow automation and customization
- Competence in information security and data privacy practices
- Ability to perform system audits and compliance checks
- Proficiency in document editing and formatting tools (e.g., Adobe Acrobat, Microsoft Office Suite)
- Basic IT troubleshooting and technical support skills
- Depending on the organization and position, they may also need skills related to clinical documentation, HIPAA, construction documents, legal documents, Good Manufacturing Practices, etc.
- Archives and libraries
- Schools, colleges, universities, research institutions, etc.
- 엔지니어링 회사
- 금융 기관
- 정부 기관
- 의료 기관
- Law firms and consulting firms
- 비영리 단체
- Private and public companies, including retailers, pharmaceutical, and tech companies
- Publishers and news agencies
Document Management Specialists work with all departments within their organization and must collaborate on establishing and customizing workflows that suit everyone’s needs.
They don’t just handle hard-copy documents; they’re responsible for electronic documents, too. Because of this, they must master document management software and enforce data privacy and security protocols to prevent unauthorized disclosure.
This requires staying up-to-date on the latest software, scanning technologies, and digital preservation methods. They may have to troubleshoot systems, perform compliance audits, and implement disaster recovery strategies to protect organizational data.
Cloud-based solutions are becoming dominant in document management, thanks to the remote accessibility, security, and scalability they provide. Cloud storage also supports collaborative, real-time document sharing and editing.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are automating certain document-related tasks, like data entry, classification, and information extraction. They even help to improve security, compliance, and search functionalities.
Sustainability is increasingly important, so organizations are adopting digital systems to reduce paper use and storage needs, cutting down their environmental impact. Electronic signatures and digital receipts are reducing paper dependence, too!
Document Management Specialists tend to be organized, analytical, and efficient. In their younger days, they may have been tidy, enjoyed reading, or playing games that require critical thinking. They might have been equally comfortable by themselves as they were participating in group activities.
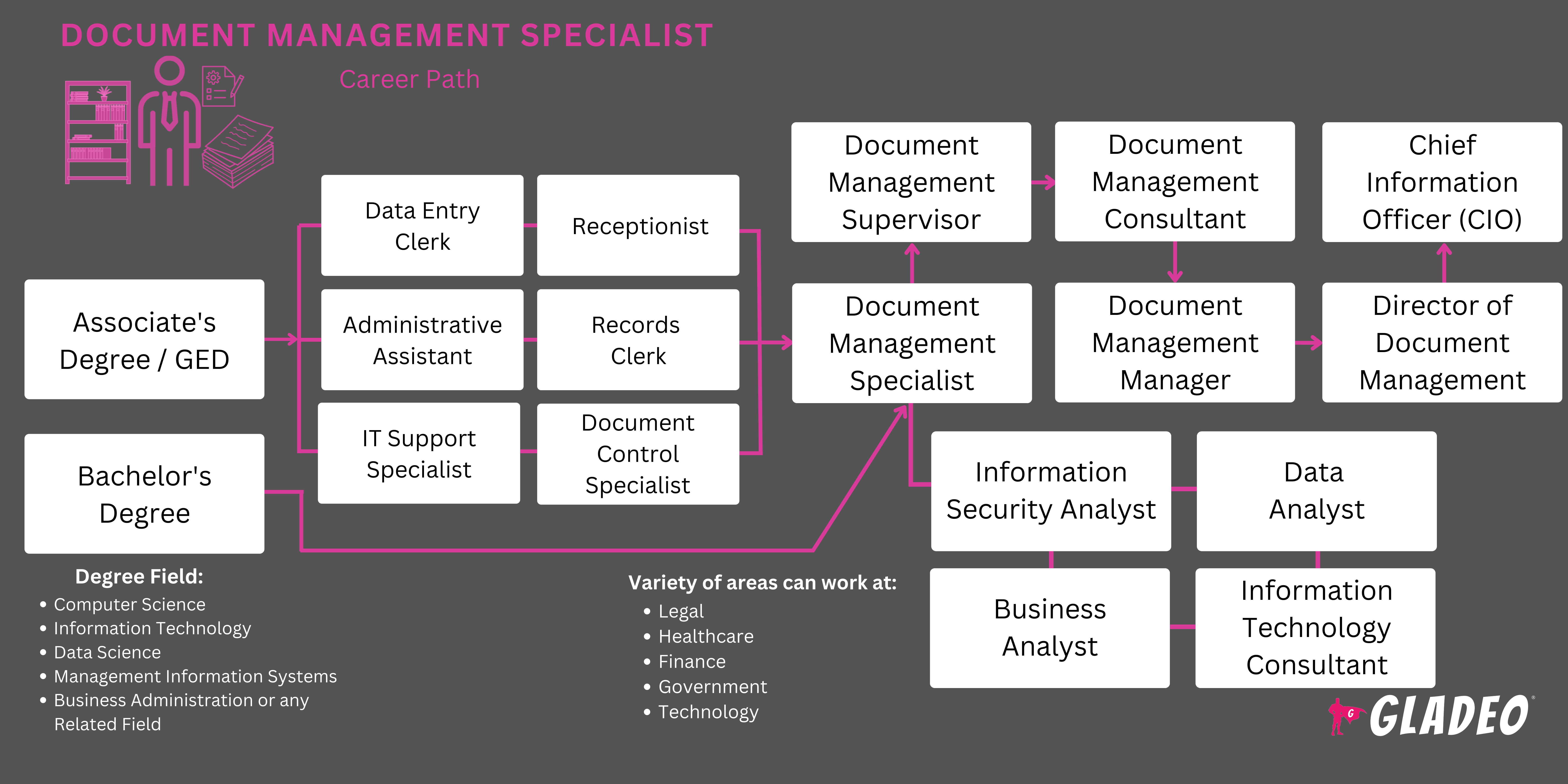
- Roughly half of workers in this field have a bachelor’s degree, while some get started with an associate’s
- Common majors include business, English, Library Science, Information Management, Information Technology, and Computer Information Systems
- Document Management Specialists receive additional On-the-Job training as well
- 선택적 인증에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- American Academy of Professional Coders - Certified Documentation Expert Outpatient
- American Health Information Management Association - Certified Documentation Integrity Practitioner
- Association for Healthcare Documentation Integrity - Certified Healthcare Documentation Specialist
- Association of Clinical Documentation Improvement Specialists -
• Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist
- Center for Professional Innovation and Education - Document Management Certification
- Computing Technology Industry Association (CompTIA) - CompTIA Cloud Essentials
- Consepsys - Document Control Professionals
- Construction Specifications Institute - Construction Documents Technologist
- Defense Intelligence Agency PMO - Certified Collection Management Professional
- EC-Council - EC-Council Disaster Recovery Professional
- Institute of Certified Records Managers - Certified Records Analyst and Certified Records Manager
- Look for programs with a focus on information technology, document management systems, and records management.
- Consider the program’s cost and the availability of financial aid or scholarships.
- 주 내 수업료와 타주 수업료 및 수수료에 유의하세요.
- Check the program’s statistics regarding employment rates for graduates.
- See if they have any connections with local employers who may hire recent grads.
- Focus on courses in computer science, information technology, and business administration classes
- Prepare for college by taking relevant Advanced Placement classes
- Seek internships or part-time jobs related to filing, administrative assistance, document control, and records management. Relevant positions might include:
- Document Clerk
- 행정 보조원
- 기록 관리자
- Library Technician
- 법무 장관
- Information Systems Manager
- Join technology or business clubs to enhance your knowledge and network with professionals
- Enroll in some non-degree courses on Udemy, Coursera, or LinkedIn Learning related to document or content management systems and tools
- Volunteer to do document management tasks at your school
- 이력서를 위해 업적, 프로젝트, 기술을 기록해 두세요.
- Keep your record clean in case you need to go through a background check to get a security clearance
- Maintain a professional digital footprint on social media
- 추천인 역할을 할 사람을 결정합니다. 추천인에게 연락처 정보 제공에 대한 허락을 구합니다.
- 학교의 커리어 센터를 방문하여 이력서 작성 및 모의 면접에 대한 도움을 받으세요.
- Review job postings on Indeed, Glassdoor, USAJOBS, and other job portals
- Note the keywords in job ads. Try to incorporate them into your resume where possible. Popular keywords might include:
- Compliance Management
- Content Management
- Data Privacy & Security
- Digital Archiving
- Document Management Systems
- Enterprise Content Management
- Information Governance
- Metadata Classification
- Records Retention Policies
- Workflow Automation
- Take a look at templates for Document Management Specialist resumes
- Review apprenticeship opportunities for Document Management Specialists
- Review Document Management Specialist interview questions such as “What kind of software programs have you used to upload, sort, and store informational documents?”
- 친구들과 함께 모의 면접을 통해 답변 연습하기
- Dress professionally for interviews!
- Network with professionals in the field. Ask for tips about job openings
- Talk with your supervisor about which professional development courses you could take to benefit the organization
- Pursue advanced or specialized certifications related to the industry you’re in
- For example, Microsoft 365 Certified: Fundamentals could be a valuable certification if your employer uses (or wants to use) SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Teams, which are extensively used for document management and collaboration
- Consider earning a master’s degree to qualify for a promotion.
Feasible options may include:
- Master of Business Administration
- Master of Science in Information Management
- Master of Library and Information Science
- Master of Science in Knowledge Management
- Master of Science in Management Information Systems
- Establish a reputation as an efficient specialist who keeps things organized and secure
- Follow all organizational, state, and federal guidelines related to data privacy
- Teach your organization’s employees how to safeguard documents properly
- Participate in professional organizations like ARMA International or the Institute of Certified Records Managers to network and learn about new opportunities
- Volunteer to take on more responsibilities, including supervising others
- Find someone willing to mentor you about career progression
- Consider relocating or looking for jobs at larger organizations to advance your career
웹사이트
- Access Corp
- Adobe
- AGS Record Management
- 미국 건강 정보 관리 협회
- ARMA International
- Association for Intelligent Information Management
- 컴프티아
- Exela Technologies
- GRM Document Management
- Hyland Software
- IBM Corporation
- 공인 기록 관리자 협회
- International Council on Archives
- International Secure Information Governance & Management Association
- Iron Mountain
- Konica Minolta
- Kyocera Document Solutions
- 마이크로 소프트
- National Archives
- Open Text
- Oracle Corporation
- Pacific Records Management
- 프로젝트 관리
- Record Nations
- Society of American Archivists
- Vital Records Control
- Xerox
책
- Document Control: Lifecycle and the Governance Challenge, by Dawit Kassa
- Engineering Document Control, Correspondence and Information Management for All, by Huw Grossmith
- Sharepoint: Efficient Document Management, Version Control, and Libraries in Sharepoint, by Lynn Brown
Document Management Specialists are key workers in any organization, but if you’re looking for some alternatives, check out a few of the related occupations below!
- 관리 서비스 관리자
- 컴퓨터 시스템 분석가
- 데이터베이스 관리자
- 데이터베이스 설계자
- Health Information Technologist and Medical Registrar
- 정보 보안 분석가
- 경영 분석가
- 의료 기록 전문가
- 프로그래머
- Web Administrator
뉴스 피드
주요 채용 정보

온라인 과정 및 도구





